Datacenter Vs Residential Proxies Demystified
Hey, do you know what proxies are?
Proxies act as intermediaries that hide your IP address while connecting to the internet.
Bet you already know the basics since you’re here curious about the difference between residential and datacenter proxies. It’s a bit of a deeper question, isn’t it?
Before we dive into the specifics, let’s take an overview of datacenter proxies and residential proxies. Datacenter proxies originate from data centers, large-scale facilities that house servers used to manage and store data. These proxies are not affiliated with Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and are instead linked to data centers. Residential proxies, on the other hand, are IP addresses that belong to actual residential devices. They are provided by Internet Service Providers and are usually more expensive than datacenter proxies.
While residential and dedicated proxy IPs both do the job of hiding your IP, they come with some key differences. Let’s break it down and find out which one is the best fit for you.
What Are Datacenter Proxies?
Datacenter Proxies are specialized proxies that are not linked to any Internet Service Provider (ISP). Instead, they are sourced from secondary corporations that own the infrastructure to generate these proxies, ensuring you benefit from completely private IP authentication and anonymity. These proxies are essentially IP addresses created by data centers, which house vast amounts of computing power and bandwidth. Unlike residential proxies that are associated with individual users or physical homes, datacenter proxies are generated en masse and do not have a specific geographical location tied to them.
This makes them a popular choice for a variety of online activities, particularly those that require high speed and scalability. For instance, marketers often utilize datacenter proxies for web scraping, data mining, or managing multiple social media accounts, as they can handle large-scale requests with efficiency. Additionally, because they are not tied to residential addresses, datacenter proxies can help users bypass geographical restrictions and access content that may be blocked in their region. Overall, the versatility and performance of datacenter proxies make them an essential tool for many businesses and individuals looking to enhance their online operations.
How Datacenter Proxies Function
Datacenter proxies provide a straightforward model for understanding how proxies operate. Typically, there’s no requirement to reroute client requests through multiple devices, as the proxy server itself suffices.
When you send a request to a website via a datacenter proxy, the request passes through the proxy server. This server removes your original IP address and replaces it with a different one before forwarding the request to the intended website. Once the website processes the request, the response is sent back to the proxy, which then relays it to you.
Because your IP address is concealed during this process, the website remains unaware that the request originated from you, believing instead that it came from the proxy server.
Pros of Datacenter Proxies
High Speed and Reliability:
Datacenter proxies are known for their blazing-fast speeds. Since they originate from high-capacity servers, they provide consistent and reliable performance, making them ideal for tasks that demand quick data processing.
Scalability:
One of the significant advantages of datacenter proxies is their scalability. Businesses can easily acquire thousands of these proxies, making them perfect for large-scale operations like web scraping, where multiple IP addresses are needed.
Cost-Effective:
Compared to residential proxies, datacenter proxies are generally more affordable. This cost-effectiveness makes them accessible for startups and small businesses looking to optimize their online activities without breaking the bank.
Cons of Datacenter Proxies
Susceptible to Detection:
Due to their non-residential nature, datacenter proxies are easier to detect. Websites and services can identify and block them, especially if they’re used in high volumes.
Limited Flexibility:
While datacenter proxies are excellent for certain tasks, they lack the flexibility of residential proxies. They may not be suitable for activities requiring a more authentic user experience, such as managing social media accounts.
What Are Residential Proxies?
Residential proxies are IP addresses assigned to real residential locations by ISPs. These proxies appear as legitimate home users, making them harder to detect and block. These IP addresses can originate from a wide array of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices, each contributing to the diversity of the proxy pool. This variety not only enhances the authenticity of web requests but also facilitates smoother interactions with websites that implement strict geo-location restrictions.
The nature of residential IP addresses makes them ideal for automation tasks that require bypassing geo-location and ensuring high levels of anonymity. Unlike datacenter proxies, which can be easily detected and blocked, residential proxies offer a more discreet approach, effectively mimicking the behavior of real users. This capability allows businesses and individuals to access region-specific content, conduct market research, or scrape data without raising suspicion.
Furthermore, residential proxies are particularly adept at navigating stringent anti-proxy measures employed by many websites. Their ability to blend in with genuine user traffic significantly reduces the likelihood of being flagged or banned, making them an invaluable tool for those who rely on web scraping, social media automation, or other online activities that require a high degree of privacy and reliability.
Understanding How Rotating Residential Proxies Function
Residential proxy providers maintain a vast pool of IP addresses. When you send a web request via their servers, they select one of the available IPs from their pool to route your request to the desired website.
With rotating residential proxies, the IP addresses used for your connection change either with each web request or after a predetermined period.
Session-Based Rotation
In session or request-based rotation, each web request you send is directed through a different IP address. This method is particularly useful for web scraping, where numerous requests are made per minute. By utilizing this rotation strategy, websites remain unaware of any unusual activity, significantly reducing the chances of raising suspicion.
Time (sticky session)
However, in the case of IP rotation by time, the IP address gives you access to changes after a period of time. This is most important in social media automation bots like IG bots and FollowLiker, as well as sneaker bots, for you have to need more sticky session time with the same IP.
Pros of Residential Proxies
Better Detection Avoidance:
Residential proxies excel in avoiding detection. Because they mimic real user behavior, websites and services find it challenging to identify them as proxies, allowing for smoother, uninterrupted browsing.
More Realistic Behavior:
These proxies offer a more authentic user experience. They are ideal for tasks that require genuine interactions, such as social media marketing or e-commerce activities.
Diverse IP Pools:
Residential proxies come from a wide range of locations, providing a diverse IP pool. This diversity is beneficial for activities that require access to geo-restricted content or localized market research.
Cons of Residential Proxies
Slower Speeds:
Residential proxies tend to be slower compared to their datacenter counterparts. Since they rely on regular household connections, their performance can vary based on the ISP and location.
Higher Costs:
These proxies are typically more expensive due to their complexity and the higher demand for their authentic nature. Businesses need to weigh the benefits against the costs before opting for residential proxies.
Limited Availability:
Finding reliable residential proxies can be challenging. Their limited availability often leads to higher prices and competition among businesses seeking these valuable resources.
Key Differences Between Datacenter and Residential Proxies
| Aspect | Datacenter Proxies | Residential Proxies |
| IP Origin | Come from data centers | Tied to residential IP addresses assigned by ISPs |
| Detection Risk | More likely to be flagged by websites | Resemble real user traffic, less likely to be detected |
| Speed and Reliability | High-capacity servers ensure quick data processing | More authentic but may lag in performance |
| Cost | Generally more affordable, cost-effective for bulk operations | Higher authenticity comes at a premium price |
| Use Cases | Ideal for web scraping, bulk data collection, tasks requiring speed | Better for social media marketing, account creation, activities needing genuine user interactions |
Choosing the Right Proxy
When you’re trying to choose between datacenter proxies and residential IPs, think about what you’ll be doing online. Datacenter proxies usually work well for most people, especially if you use fingerprint masking tools like GeeLark. But, if your browser fingerprint isn’t masked right, you could get flagged by security systems. Some platforms, such as Craigslist, strictly prohibit datacenter proxies to prevent spam, making residential IPs the better option in such cases. All in all, datacenter proxies can do the job if you mask properly, but there are times when residential IPs are a must to avoid detection.
When to Choose Datacenter Proxies
- For high-performance tasks: When speed and bandwidth are critical, datacenter proxies offer a significant advantage.
- For large-scale operations: For bulk operations, the scalability and performance of datacenter proxies make them a suitable choice.
- For cost-effectiveness: Datacenter proxies often offer a more affordable option, especially for high-volume usage.
- For web scraping: Using datacenter proxies, you can efficiently collect vast amounts of data without worrying about speed limitations. However, you may need to rotate proxies frequently to avoid detection.
When to Go for Residential Proxies
- To avoid detection: When it’s essential to bypass geo-restrictions, avoid CAPTCHAs, or minimize the risk of being flagged as a bot, residential proxies provide a significant advantage.
- For a better user experience: For tasks that require a more human-like browsing experience, such as social media marketing or e-commerce, residential proxies are ideal.
- For privacy and security: When protecting your privacy and avoiding detection is a priority, residential proxies can be a valuable tool.
How to Set Up Proxies in GeeLark
Before creating your cloud phone profiles, it’s essential to set up your proxies first. Follow this simple guide for a smooth setup:
- Select the appropriate proxy type that suits your needs.
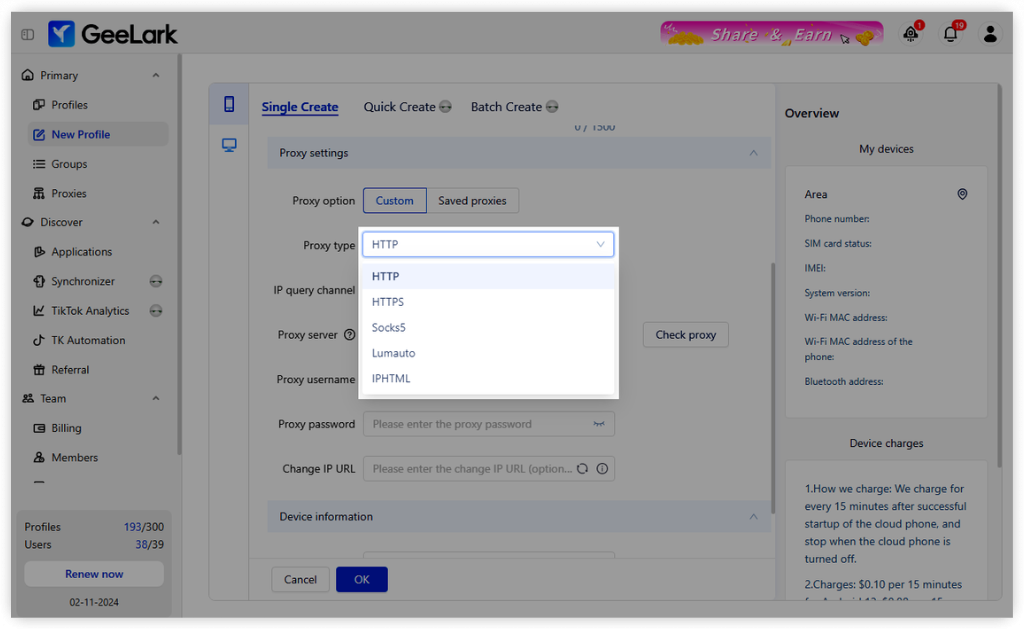
- Configure your proxy settings in GeeLark to ensure seamless integration with your mobile device.
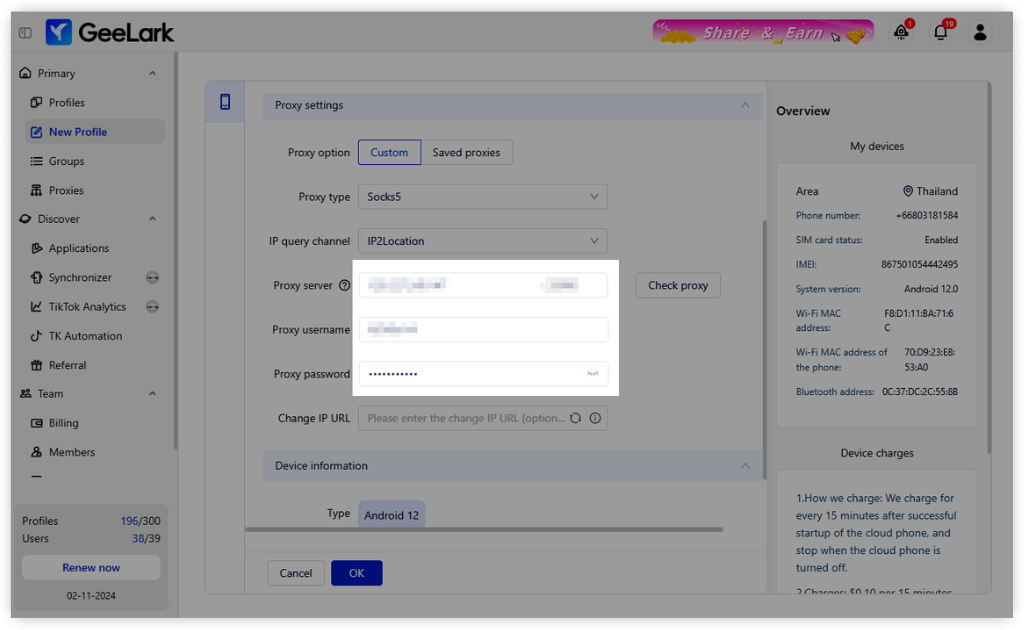
- Click on “Check Proxy” to verify your connection.
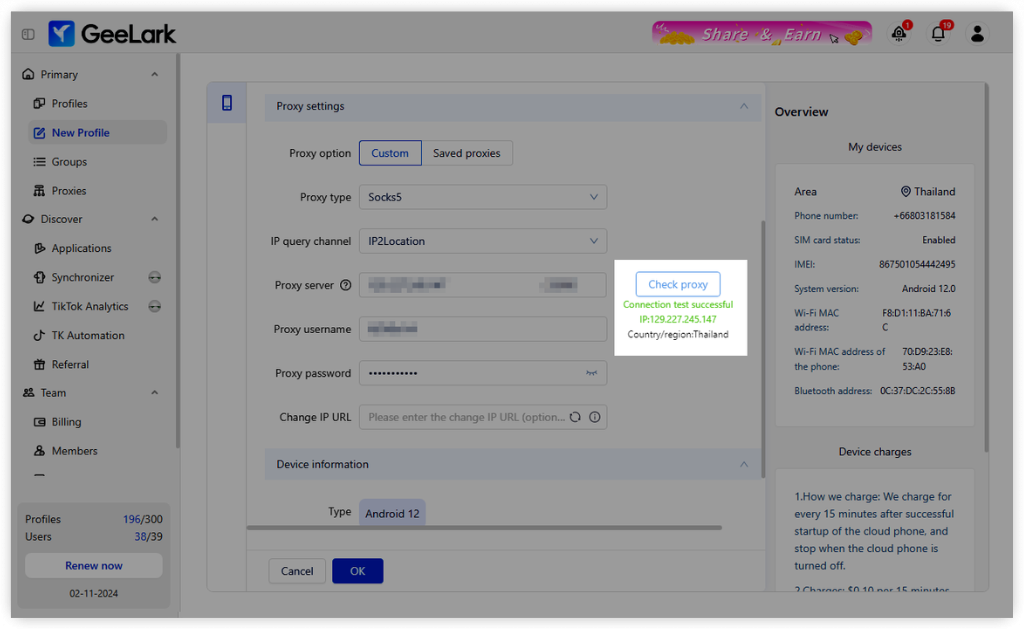
Once everything is set, just hit OK to finalize the settings, and you’re ready to start using your cloud phones!
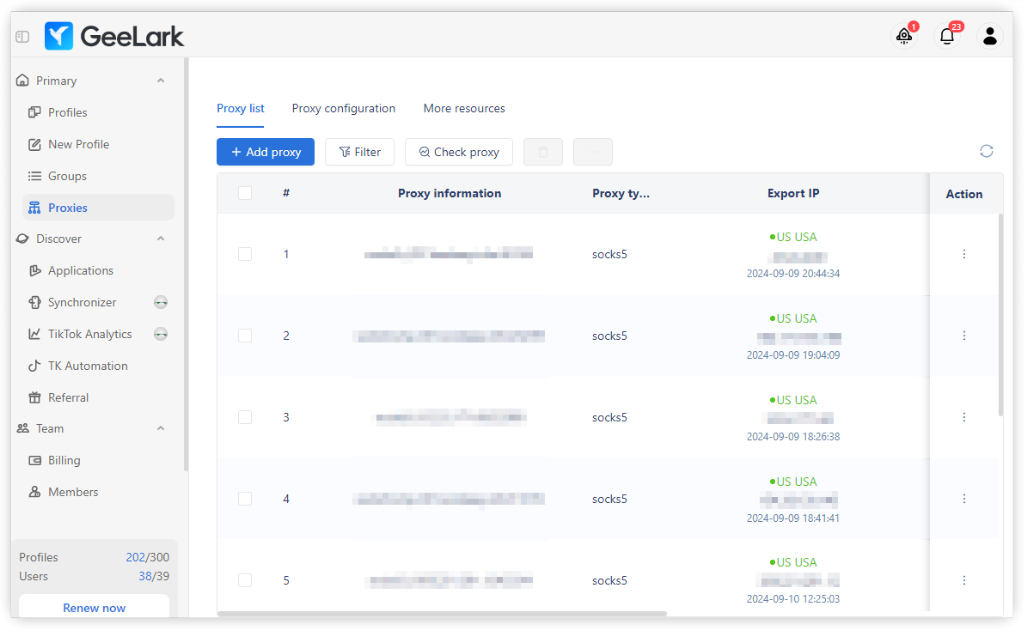
You can easily view your proxy list and configuration details in the Proxies menu. Additionally, if you’re looking to speed up your product hunting, explore the More Resources section within the GeeLark app to find suitable proxy servers.
FAQs
What is the main difference between datacenter and residential proxies?
Datacenter proxies are based in data centers, offering high speed and performance but are more likely to be detected. Residential proxies use real residential IP addresses, providing better anonymity but may be slower.
Can I use both datacenter and residential proxies together?
Yes, you can use a hybrid approach, combining the advantages of both types.
What is IP rotation?
IP rotation is the process of automatically switching between different IP addresses to avoid detection.
Which proxy is better for mobile anti-detect?
Residential proxies are generally better for mobile anti-detect due to their enhanced anonymity and natural browsing experience. While datacenter proxies can offer faster speeds and higher bandwidth, they are more likely to be detected due to their shared IP addresses and distinct patterns of usage. This can make them less effective for mobile anti-detect.








