SOCKS Proxy Explained: What it is and How to use
What Are SOCKS and SOCKS Proxies?
What Is SOCKS?
SOCKS, which stands for Socket Secure, is a method to transfer data between your computer and a server on the internet. You can think of it as a middleman that routes your internet traffic through a proxy server before reaching its final destination. This process helps you get around firewalls while keeping your real IP address hidden, thereby providing greater privacy.
One of the main features of SOCKS is that it employs the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to establish connections to the destination server. Once a connection is made, it facilitates sending and receiving data packets between you and the server. Notably, a significant advantage of SOCKS is its versatility, as it can handle many types of internet traffic created by various software and protocols. This makes it ideal for heavy-duty tasks like streaming videos and peer-to-peer sharing.
SOCKS is classified as a layer 5 protocol in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. Consequently, it can manage protocols working at layer 5 and higher, such as HTTP, HTTPS, POP3, SMTP, and FTP. Because of its position within the OSI model, SOCKS can effectively handle these requests, providing secure and anonymous connections for a wide range of applications.
What Is a SOCKS Proxy?
When you utilize a SOCKS proxy, your internet traffic is transmitted through a third-party server. This effectively hides your real IP address and assigns you a new one, complicating the ability of websites to determine your actual location.
SOCKS operates on Layer 5 of the OSI model, which means it helps manage the connection between your computer and the internet. Moreover, the newest version, SOCKS5, supports both UDP and TCP connections, offering enhanced options and better security compared to the older version, SOCKS4.
SOCKS4 Proxy vs. SOCKS5 Proxy
SOCKS4 Proxy
SOCKS4 is an older type of SOCKS protocol. It primarily supports TCP connections, which are used for reliable data transfer over the internet. The main role of a SOCKS4 proxy is to route your internet traffic through a proxy server to conceal your real IP address.
However, SOCKS4 proxies come with certain limitations. For instance, it does not support UDP proxies, which are essential for activities such as video streaming and online gaming. Additionally, SOCKS4 lacks mechanisms for authentication via a username and password.
SOCKS5 Proxy
SOCKS5 represents the newer version of the SOCKS protocol, equipped with more features than SOCKS4. Importantly, it supports both TCP and UDP connections, thereby enhancing versatility for various internet activities.
Furthermore, SOCKS5 allows for authentication using a username and password, which adds an extra layer of security. Additionally, SOCKS5 can manage both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, making it better suited for contemporary internet technologies.
HTTP Proxy vs. SOCKS Proxy
Understanding the distinctions between HTTP proxies and SOCKS proxies is crucial when making the right choice based on your needs. Below, we summarize the main differences regarding security, functionality, performance, speed, compatibility, and operability.
Security
- HTTP Proxy: Operates at a higher security level, adds a layer of protection, can detect and block suspicious data, and understands data transferred between client and server.
- SOCKS Proxy: SOCKS5 offers encrypted SSH tunneling for data privacy without interpreting the data. SOCKS4 is generally less secure.
Functionality
- HTTP Proxy: Handles only HTTP(S) traffic, can cache responses, and detect repeated requests, making it suitable for web-related tasks.
- SOCKS Proxy: Handles various network protocols without interpreting the data, making it suitable for a broader range of applications, including those requiring firewall access.
Performance
- HTTP Proxy: Enhances performance by caching web pages and filtering data. Speed varies by type (public, shared, private), with private proxies being the fastest.
- SOCKS Proxy: Generally faster because of reduced computational overhead. SOCKS5 utilizes the UDP protocol for even faster processing.
Speed
- HTTP Proxy: Speed depends on type; public proxies are slower, shared ones can be faster, while private proxies provide maximum speed.
- SOCKS Proxy: Typically faster due to less code execution time. SOCKS5 operates even faster with the UDP protocol. For those seeking robust residential proxy services with SOCKS5 and UDP support, consider Mangoproxy. Mangoproxy offers over 90 million IP addresses across 220+ countries, complete anonymity, unlimited concurrent sessions, and flexible pricing with precise geotargeting. Their easy integration and 24/7 live support make them a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes.
Compatibility
- HTTP Proxy: Exclusively works with HTTP protocol, supports ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS), and connects with a variety of third-party tools.
- SOCKS Proxy: Operates in different environments, handles various traffic types, supports ports 1080 and 1081, and can operate on any port.
Operability
- HTTP Proxy: Limited to a single protocol but has many applications, including detecting inconsistencies in cache requests and responses.
- SOCKS Proxy: Offers greater compatibility, works with multiple protocols, is flexible, and provides access even behind a firewall.
Which Choice Is the Best for You?
Choosing between HTTP and SOCKS proxies ultimately depends on your requirements. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you determine which option might be best for you.
HTTP proxies are best suited for web browsing and managing web traffic (HTTP/HTTPS). They offer high security levels while improving performance through caching and data filtering. Consequently, this makes them ideal for applications requiring detailed data analysis and filtering, such as email protection and web data gathering (web scraping). If your primary goal is to ensure secure and efficient web browsing while analyzing and filtering data, an HTTP proxy would be a suitable choice.
Conversely, SOCKS proxies are more versatile and can handle various types of internet traffic, not just web data. Generally, they offer simpler and faster operations, making them suitable for high-speed data transfers and applications where bypassing firewalls is essential. Therefore, SOCKS proxies are preferred when speed and flexibility take priority over detailed data filtering. If you seek a proxy that can quickly transfer data and navigate around firewalls, a SOCKS proxy is the better option.
Additionally, many proxy service providers support both HTTP(S) and SOCKS5 connections, allowing users to switch between them according to their specific requirements. This flexibility ensures that you can choose the most appropriate proxy type to meet your needs, whether it be for security, functionality, or performance. By understanding these differences, you can make a more informed choice that aligns with your objectives.
Set Up SOCKS Proxies in GeeLark
To set up SOCKS proxies in GeeLark, follow these simple steps.
1. Choose Proxy Type: Select “Socks5” from the list.
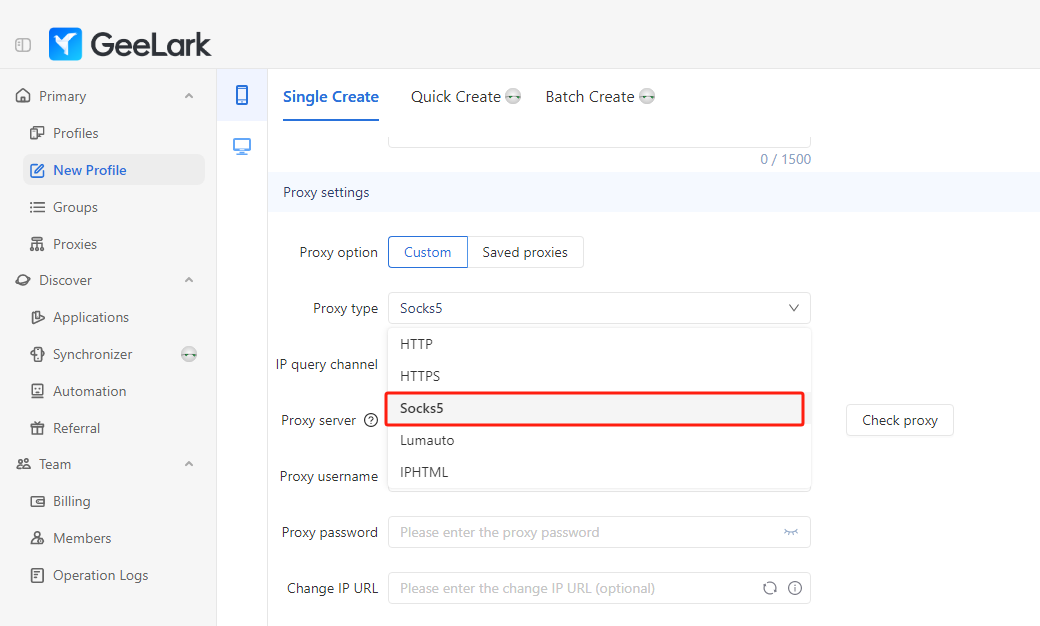
2. Enter SOCKS5 Proxy Information and click “Check Proxy.” You can then confirm the proxy to view the IP address alongside its country and ISP details.
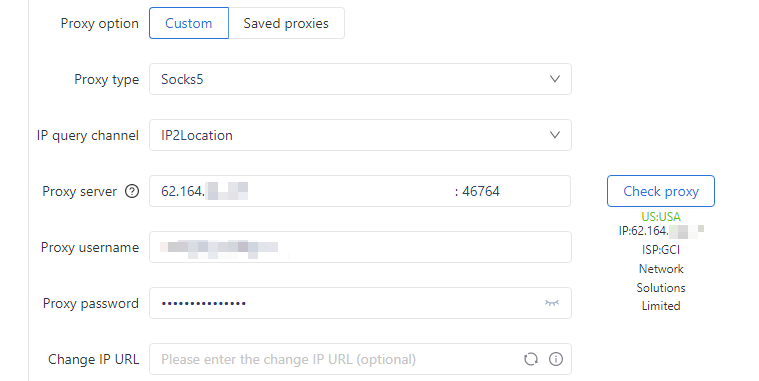
Once everything is set, simply hit OK to finalize the settings, and you’re ready to start using your cloud phones!
What Is GeeLark?
GeeLark is transforming how you manage multiple accounts with its innovative antidetect technology. Unlike regular antidetect browsers, GeeLark provides complete Android environments, not just browsers. As a result, you can create many cloud phone profiles, each with its unique digital fingerprint.
If you need to manage multiple Telegram, Facebook, TikTok, or mobile game accounts without worrying about bans, GeeLark is an excellent solution.
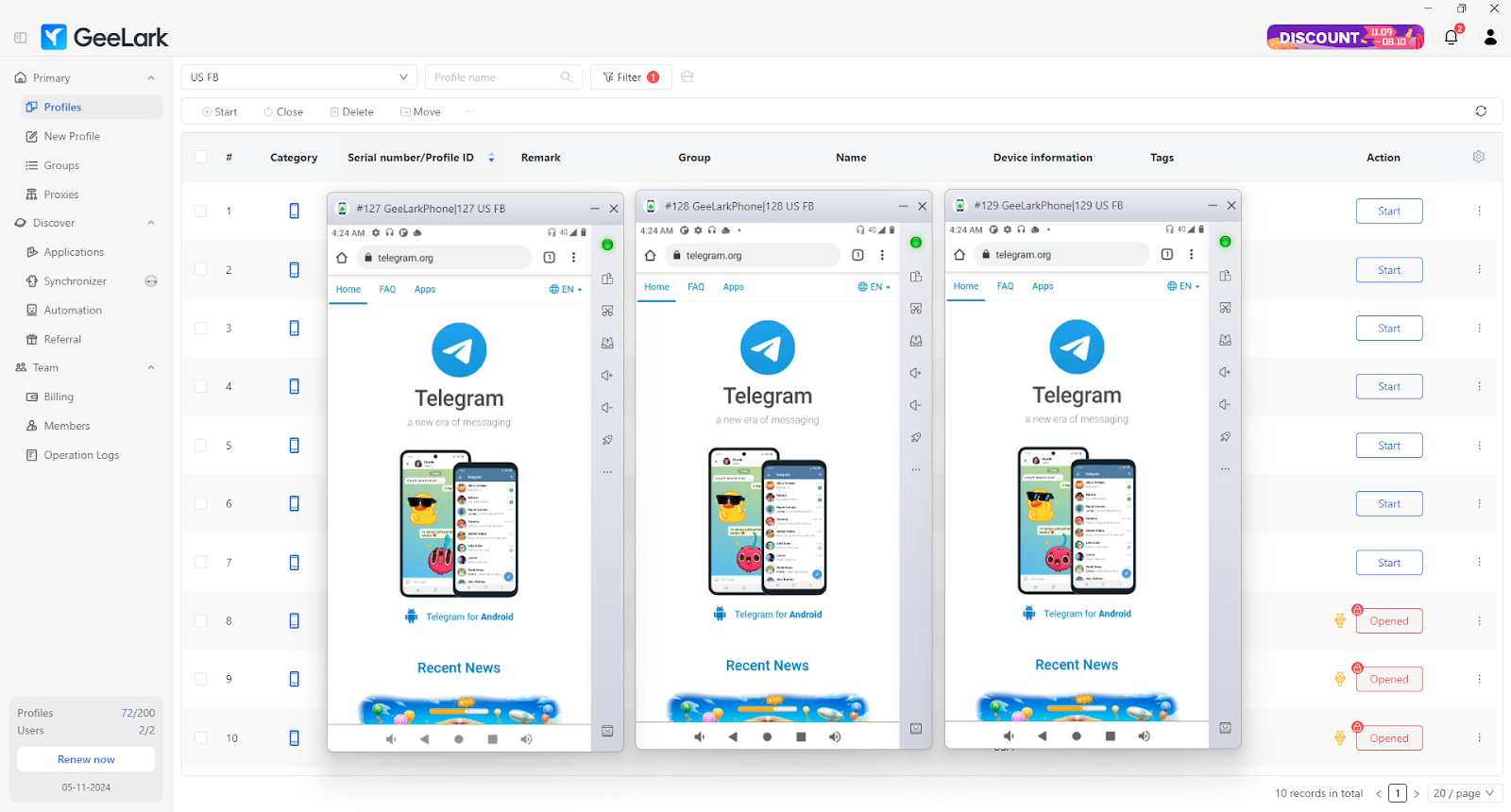
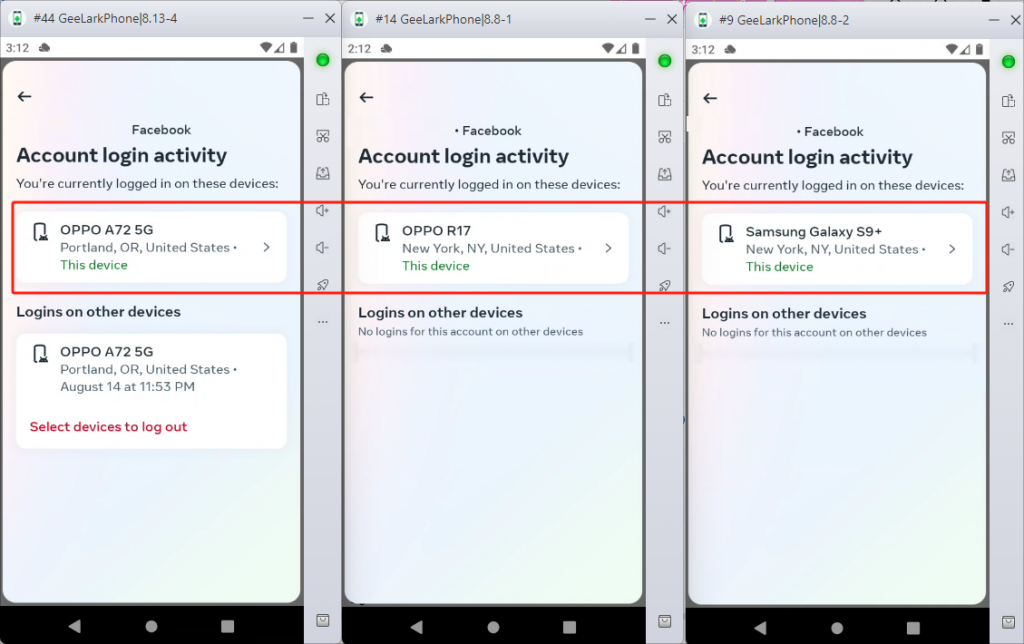
One helpful feature of GeeLark is the ability to set up and manage separate cloud phone profiles. Each profile is assigned its unique IP address (from your configured HTTP/HTTPS or SOCKS proxy), phone number, MAC address, and Bluetooth address. This setup keeps each profile distinct, ensuring that activities in one profile do not interfere with another. Thus, it helps protect your privacy and provides invisibility from tracking.
Additionally, GeeLark offers automation tools that help you avoid tedious and repeat tasks. These features streamline your work processes while maintaining security and privacy. Currently, there are automation templates designed for TikTok and Facebook. Such templates enable you to log in, edit profiles, publish videos, create image collections, warm up accounts, and post content easily.
Ready to streamline your online account management?
FAQ
1. Is it safe to use a SOCKS proxy?
The safety of utilizing a SOCKS proxy largely depends on where you obtain it, how it is configured, and the additional security measures you implement. Some reputable paid services, such as BrightData, Oxylabs, and Proxy-Seller claim to provide safety regardless of the proxy type used.
2. Which is better: TCP or UDP?
TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, is preferable when ensuring all data arrives in the correct order is crucial. Conversely, UDP, or User Datagram Protocol, excels in scenarios where speed is more important, allowing for some data loss such as those occurring in online gaming or video calls. Ultimately, your choice depends on whether you prioritize reliability or speed.
3. Which is better: SOCKS5 or HTTPS?
It is challenging to declare one as categorically better than the other, as they serve distinct purposes. SOCKS5 is utilized to route network connections through a proxy, while HTTPS focuses on securing web browsing. Your choice should hinge on your specific requirements.
4. What is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)?
Transmission Control Protocol, or TCP, comprises a set of rules governing how to initiate and maintain a conversation between computers to share data. It collaborates with the Internet Protocol (IP), which helps computers send data to one another.








